Abstract
Introduction: Bosutinib, an oral dual Src/Abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) is approved for patients with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), at a starting dose of 400 once daily (QD) in newly diagnosed patients in chronic phase (CP). Approval of first-line bosutinib was based on results from the phase 3 BFORE trial, which showed improved efficacy outcomes with bosutinib vs imatinib in this patient population. This analysis evaluated efficacy and safety of bosutinib and imatinib following dose reductions in adult patients with newly diagnosed CP CML.
Methods: This retrospective analysis included data (≥24-month follow-up) from the ongoing, open-label, phase 3 BFORE trial (NCT02130557). In all, 536 patients were randomized 1:1 to bosutinib or imatinib at a starting dose of 400 mg QD. Doses could be reduced in 100 mg decrements for toxicity; dose reductions to <200 mg QD bosutinib and <300 mg QD imatinib were not permitted. Efficacy and safety were assessed in patients who underwent dose reductions to 300 mg QD (without further reduction to 200 mg QD) or to 200 mg QD (bosutinib arm only) due to treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs). TEAEs were defined as adverse events that first occurred or worsened in severity, between the first administration of the study drug and 28 days after the last dose.
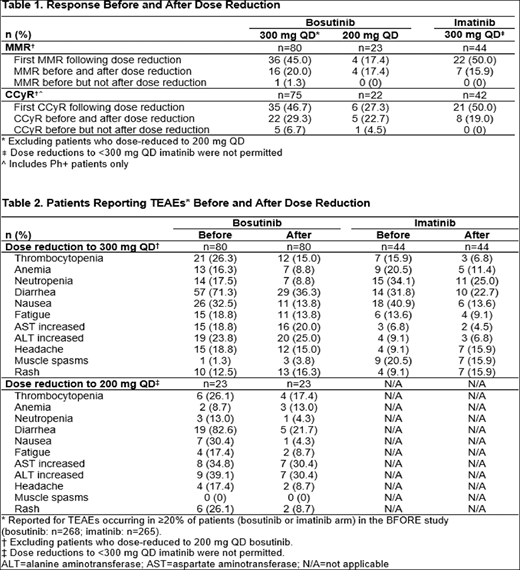
Results: Of the 268 patients in the bosutinib arm, 80 dose-reduced to 300 mg only and 23 dose-reduced to 200 mg. The median (range) overall duration of bosutinib treatment for patients dose reduced to 300 mg was 24.3 months (1.4-33.5) and to 200 mg was 8.3 months (1.0-32.9) vs. 25.1 months (range: 0.26-33.2) for patients who remained on the 400 mg starting dose. Median (range) time to bosutinib dose reduction to 300 mg was 83 days (18-793) and to 200 mg was 121 days (29-882); respective median (range) duration on reduced dose was 138.5 days (1-957) and 28 days (3-463). Of the 268 (3 untreated) patients in the imatinib arm, 44 dose-reduced to 300 mg. The median duration of imatinib treatment for patients dose reduced to 300 mg was 22.4 months (range: 1.2-33.0) vs. 24.8 months (range: 0.7-33.4) for patients who remained on 400 mg. Median time to imatinib dose reduction to 300 mg was 85.0 days (range: 15-687); median duration on reduced dose was 99.0 days (range: 2-787). TEAEs leading to dose reduction in ≥10 patients were alanine aminotransferase increased and/or aspartate aminotransferase increased (n=21), thrombocytopenia (n=19), lipase increased (n=15) and diarrhea (n=11) with bosutinib, and neutropenia (n=11) with imatinib. The most common reason for treatment discontinuation in patients who dose-reduced was a TEAE related to bosutinib (300 mg: 22.5%; 200 mg: 52.2%) or imatinib (300 mg: 27.3%). Among patients who dose-reduced to 300 mg, 16 (20%) had a major molecular response (MMR) with bosutinib before and after reduction; an additional 36 (45%) achieved MMR for the first time after dose reduction. In the imatinib arm, 7 (15.9%) had an MMR before and after reduction; an additional 22 (50%) achieved MMR for the first time after dose reduction (Table 1). 1 (1.3%) patient lost a previously attained MMR following bosutinib dose reduction to 300 mg. Among patients who dose-reduced to 200 mg bosutinib, 4 (17.4%) had an MMR before and after reduction, and an additional 4 (17.4%) achieved MMR for the first time after dose reduction. Similar trends were seen for complete cytogenetic response (CCyR) before and after dose reduction (Table 1). Among patients who remained on 400 mg, 123/165 (74.5%) had a MMR with bosutinib; 131/152 (86.2%) achieved CCyR. In the imatinib arm, 130/219 (59.4%) had a MMR and 159/198 (80.3%) achieved CCyR. The majority of TEAEs decreased in incidence with dose reduction (Table 2). Following bosutinib dose reduction to 300 mg or to 200 mg decreases >10% were seen in the incidence of diarrhea and nausea; with a decrease for rash following dose reduction to bosutinib 200 mg. Decreases (>10%) were noted for nausea following dose reduction to 300 mg imatinib.
Conclusions: Management of TEAEs through bosutinib dose reduction to 300 mg or 200 mg improved tolerability in patients with newly diagnosed CP CML. These reductions in TEAEs enabled patients to continue bosutinib treatment, with a substantial number of patients achieving MMR and CCyR for the first time after dose reduction. Findings were similar for patients who dose-reduced to 300 mg imatinib.
Brummendorf:Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy; Merck: Consultancy; Janssen: Consultancy. Gambacorti-Passerini:BMS: Consultancy; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Hochhaus:Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Incyte: Research Funding. Lipton:Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding. Kota:Pfizer: Honoraria; BMS: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria; Xcenda: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Deininger:Pfizer: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Blueprint: Consultancy. Leip:Pfizer: Employment, Equity Ownership. Viqueira:Pfizer: Employment, Equity Ownership. Ferdinand:Pfizer: Employment, Equity Ownership. Cortes:Novartis: Consultancy, Research Funding; Pfizer: Consultancy, Research Funding; Daiichi Sankyo: Consultancy, Research Funding; Astellas Pharma: Consultancy, Research Funding; Arog: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal